The starry sky in May 2025
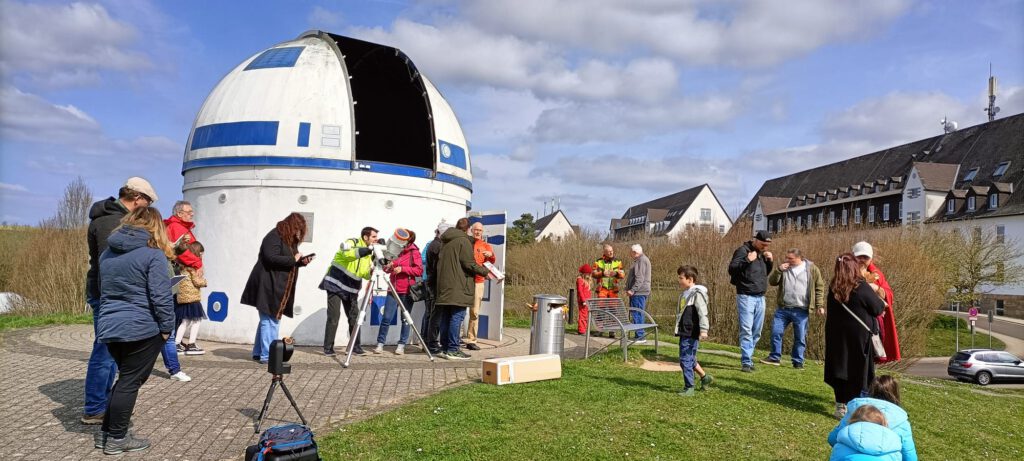
Due to the increasing length of the day, the useful observation times will be reduced from five hours at the beginning of May to just two hours at the end of the month. This would mean that the start of observations of galaxies and similar faint objects would shift from 23:00 CEST to 0:30 CEST. For this reason the observatory is only open from the beginning of May to the end of August under certain conditions. These include, for example Observation of the sun and moon on some weekends. The times are displayed via a ticker on our main page and our public WhatsApp channel announced.
SUN AND MOON
In the spring month of May, the day length for Zweibrücken increases from 14 hours and 46 minutes at the beginning to 16 hours and 4 minutes at the end of the month. The maximum elevation of the sun on May 31 is already 62 degrees.
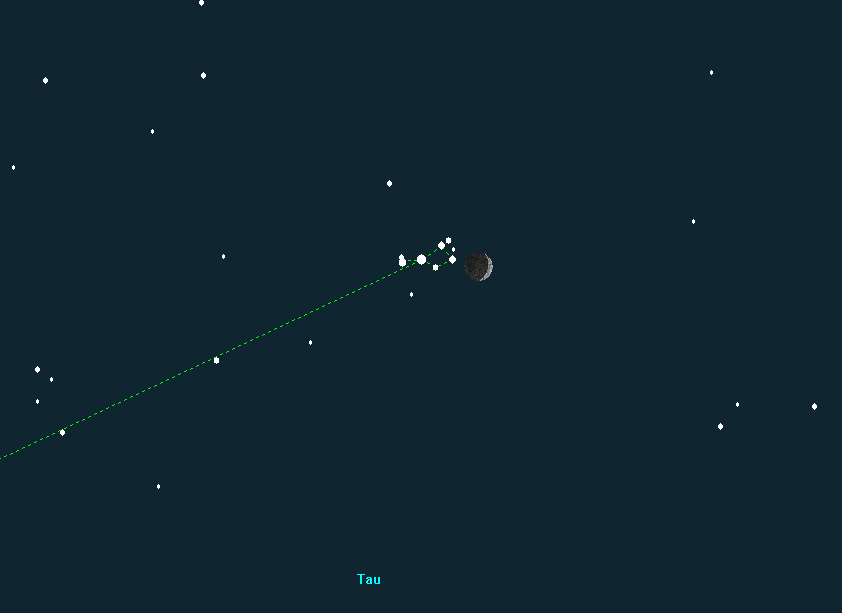
At around 1:00 a.m. on May 4, the narrow crescent of the waxing moon will pass just over one degree north of Mars. The full moon on May 12 will affect the observation of fainter objects.

PLANETS
May is poor in planets.
The planet closest to the sun, Mercury, is in superior conjunction with the sun on May 30. It is therefore in the daytime sky. Superior conjunction means that the Earth, the Sun and the object, in this case Mercury, appear to be in line. The term upper and lower conjunction is only used for Mercury and Venus.
Venus continues to expand its position as the morning star. It rises around an hour earlier over the course of the month. However, the sun also rises earlier and earlier.
Mars is long past its best observation time, having been in opposition to the Sun in mid-January.
Jupiter gives its farewell performance in the evening sky. Towards the end of the month, it is barely visible to the naked eye. It is overtaken by the sun in mid-June.
Saturn is gradually reappearing in the morning sky, but is not yet a worthwhile object for observations.
Uranus and Neptune are still not observed.
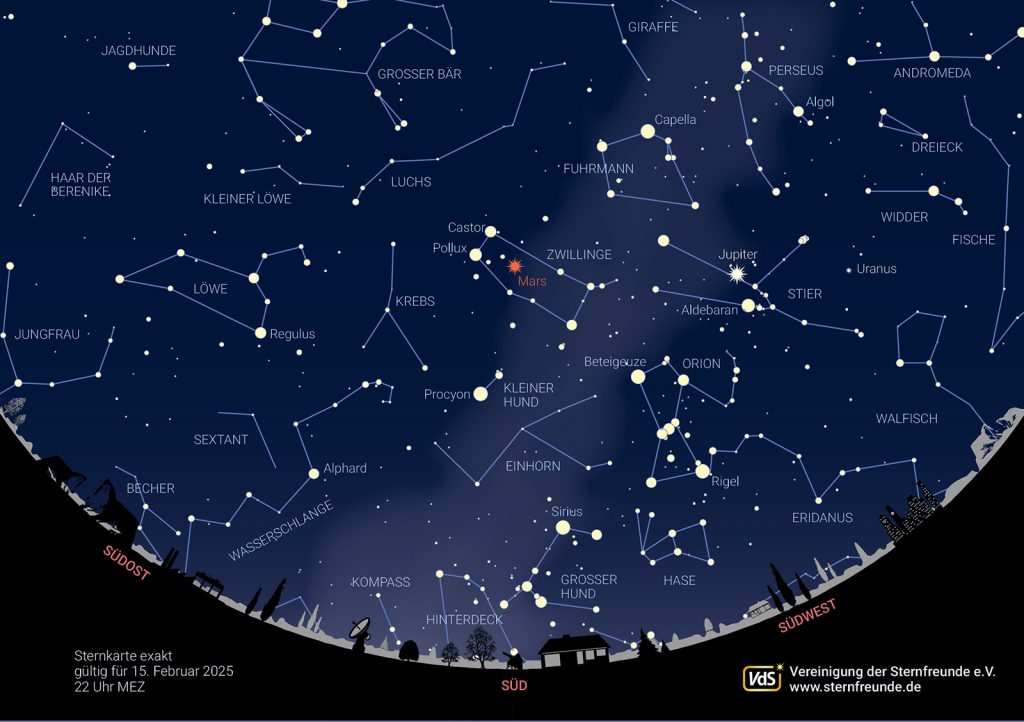
STARRY SKY
Direction West the twins are already in the process of setting. Cancer can only be observed in the haze layers near the horizon, if at all possible.
A little higher up is the lion. In Greek mythology, the lion is often associated with the hero Hercules (Heracles). According to one source, it is said to be the Nemean lion, who was up to mischief near the city of Nemea and harassed the inhabitants there. The first of Hercules' twelve tasks was to defeat the lion. However, every weapon bounced off his fur, so the Greek hero had to face the lion with his bare hands in order to defeat him. From then on, the skin protected Hercules from his enemies. At Hera's request, Zeus moved the lion to heaven.
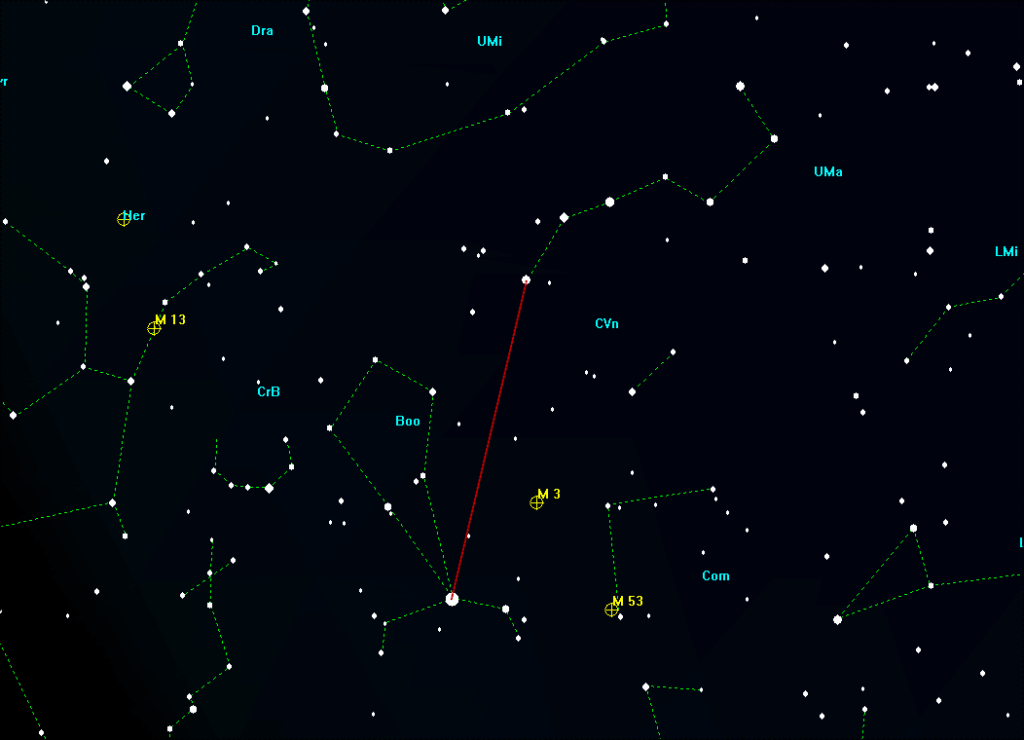
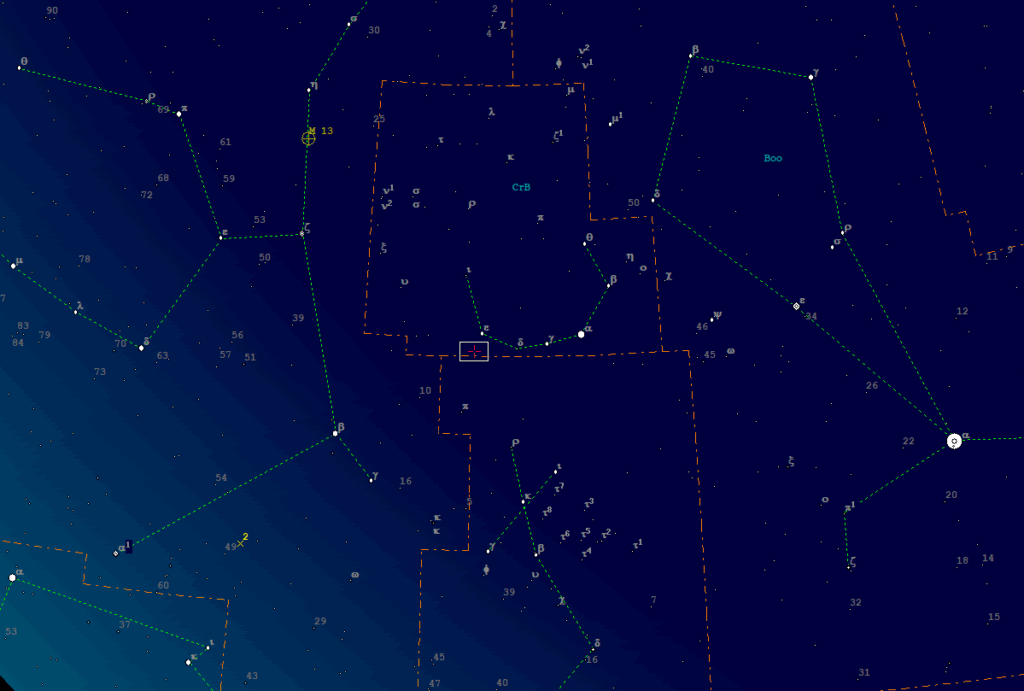
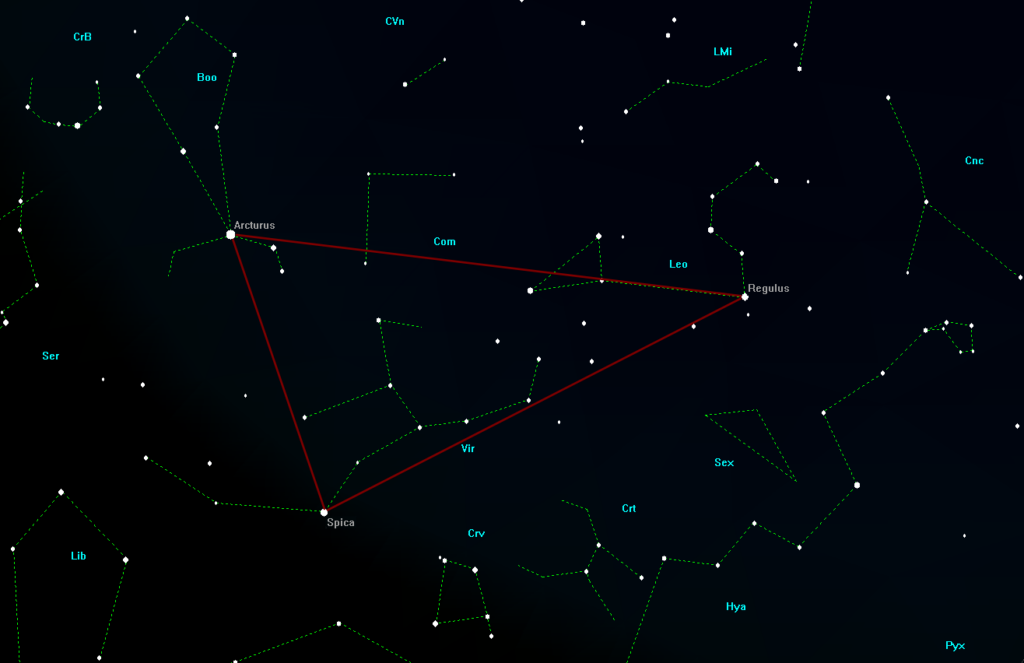
About us are the hair of Berenice with a multitude of galaxies, although a medium-sized telescope is required to observe them. A little further to the east is the Bear Keeper with its bright main star, Arcturus. A little trick makes it easier to find. If you extend the three pole stars of the "Big Dipper" in an arc, you will come across a bright star, Arcturus. To the left above the Bear Keeper is the inconspicuous constellation of the Northern Crown, where a nova has been expected since March 2024. See also the article Nova expected in the constellation of the Northern Crown. According to the latest observations, this should now appear by September 2025. Here are two graphics for orientation:
Next Eastbound you come across the inconspicuous constellation Hercules with its bright globular cluster M13, which is already a magnificent sight in binoculars. In the image above on the left.
Just above the southeastern horizon the summer constellation of Scorpius appears towards the middle of the month. The first summer constellations can be observed in the north-east.
Low on the northern night sky you can see the "celestial W", Cassiopeia, on the other side of the pole star as seen from the Great Bear.
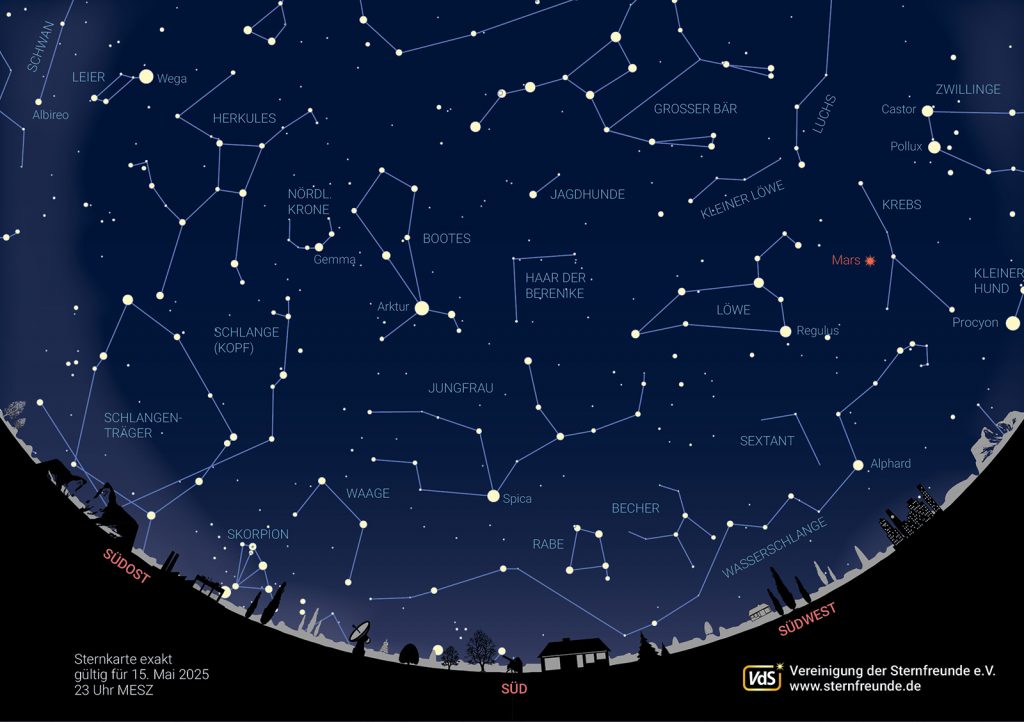
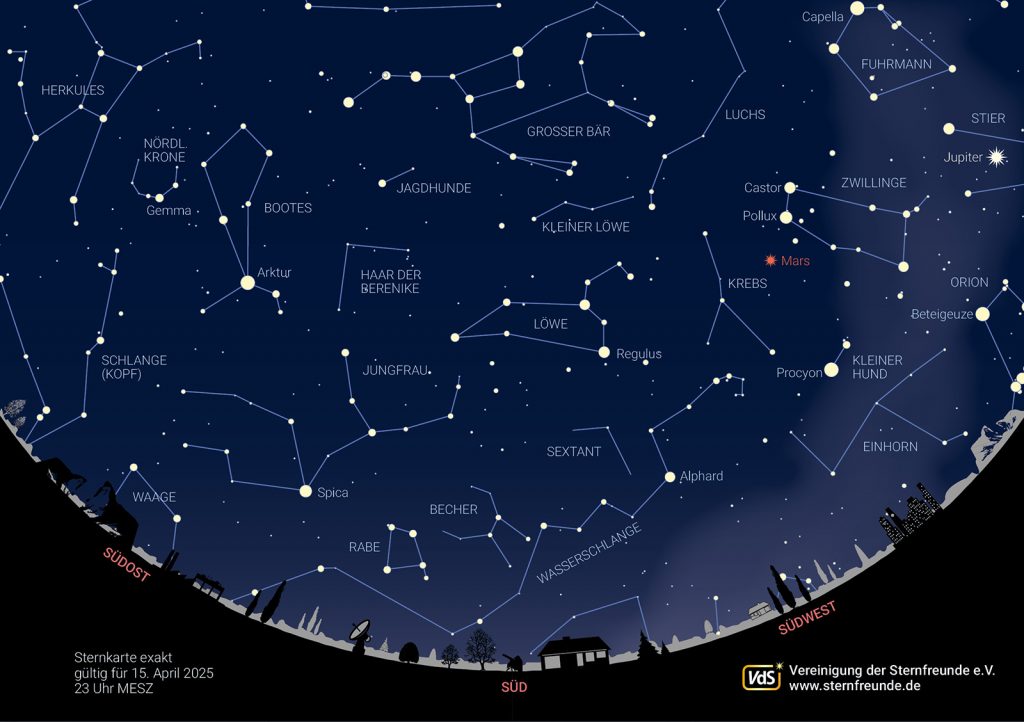
The following sky view is valid for May 1 at midnight, May 15 at 11 pm and May 30 at 10 pm.