The starry sky in December 2024
Best observation conditions for Jupiter, Venus as a bright object in the evening sky, shortest day of the year
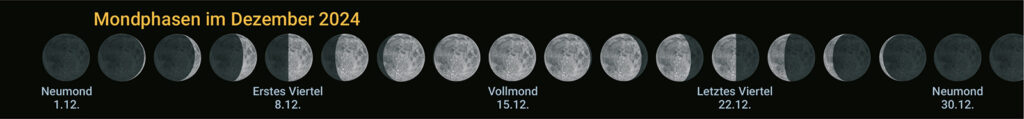
Sun and moon
The calendar date for the beginning of winter this year is December 21 at 10:21 am. On this day, the sun is at the lowest point of its orbit in the northern hemisphere. In Zweibrücken, it reaches a maximum height of just 17.25 degrees above the horizon at 12:29.
The sun rises at 8:19 a.m. and sets again at 4:38 p.m., making the day just 8 hours and 19 minutes long.
The full moon will affect the observation of fainter objects around the days of December 15.
Planets
Mercury offers morning visibility in the last third of the month. On the 25th, it reaches its greatest angular distance from the sun at a good 22 degrees. On this day, it rises at 6:29 am.
Venus becomes the radiant evening star on the south-western horizon. With its increasing brightness, it clearly outshines Jupiter, which is also visible in the evening sky. Over the course of the month, its setting times are delayed: On December 1, it sets at 19:35, at the end of the year at 20:50.
The brightness of the planet Mars increases significantly over the course of the month. After Venus, Jupiter and Sirius, it becomes the fourth brightest object in the night sky. In the telescope, its apparent diameter increases to around 14 arc seconds (one arc second corresponds to 1/3600 of a degree). The time of its rise shifts noticeably: Mars rises above the horizon at 20:30 at the beginning of the month and at 18:05 at the end of the year.
Mars reaches its opposition on January 16. In this constellation, the Sun, Earth and Mars are almost in line. Viewed from Earth, the planet is opposite the Sun and reaches a comparatively small distance from our home planet.
Reached on December 7 Jupiter its opposition position and is therefore visible throughout the night. On this day, it rises above the horizon at 4:28 pm and does not disappear again until 8:26 am. Its distance to Earth is around 4.09 astronomical units, which corresponds to around 611.9 million kilometers.
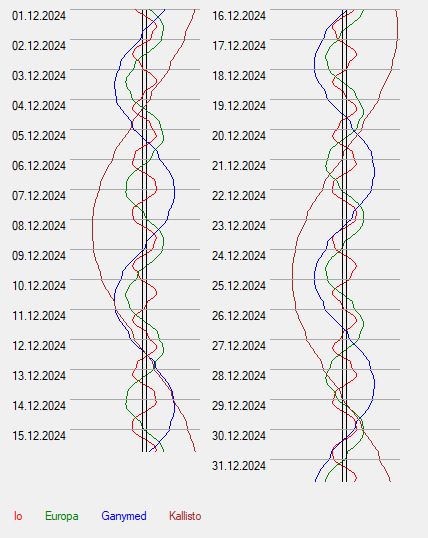
Even with an amateur telescope, the clear flattening of Jupiter's disk can be seen - an effect that is due to its high rotational speed. A day on Jupiter lasts only about 9 hours and 55 minutes. On the right is a diagram of the position of its moons.
Saturn can still be observed low in the south after nightfall, but has already left its opposition time in September far behind. On the last day of the year, it sets at 22:28.
Uranus was in opposition to the sun on November 17. As already mentioned, you need at least binoculars to observe it, or even better a telescope. You should not expect too much when looking through these devices, it has an apparent diameter of only a few arc seconds.
Starry sky
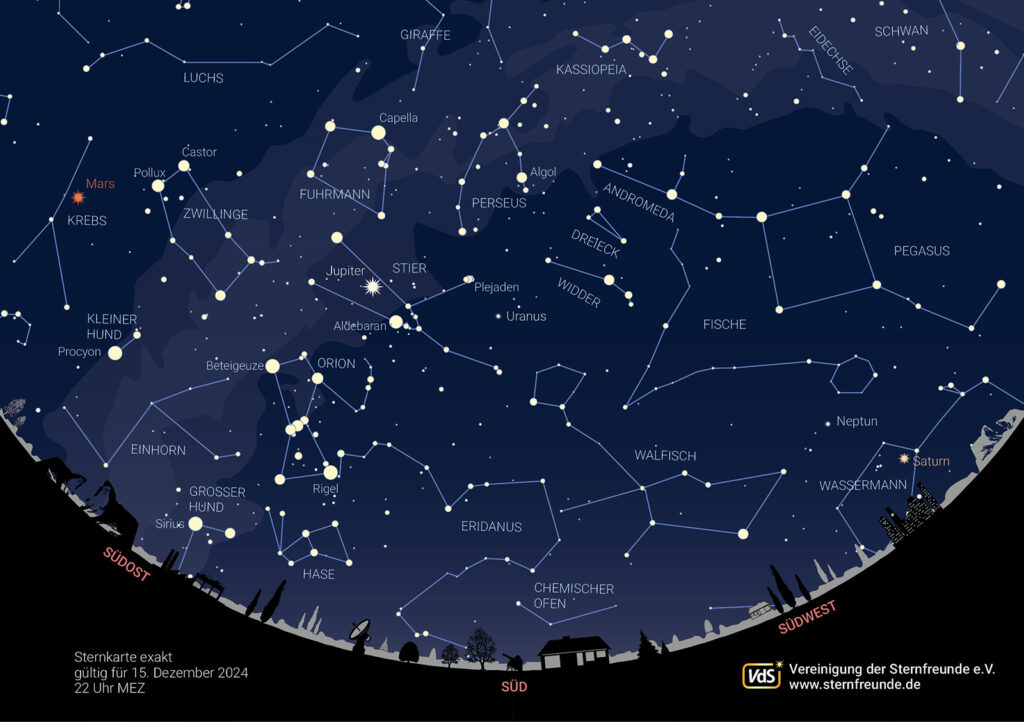
The autumn constellations move to the western night sky. They are followed in the east by the magnificent winter constellations.
On eastern horizon the sky chaser Orion can already be seen. Also the constellation Gemini.
About us is Taurus with the V-shaped horns, the Hyades, which are located south of the Pleiades. The main star of the Hyades is the striking red giant star Aldebaran.
The irregular pentagon of the carter can be found looking high towards the south, to the left above Taurus. The striking main star Capella (Latin for little goat) is the sixth brightest star in the night sky.
The southern starry sky is rather sparsely populated with stars. One of the most extensive but inconspicuous constellations, Eridanus, is located there.
In the West you can still see the striking autumnal quadrilateral, Pegasus and Andromeda. Below it is the constellation of Pisces.
On northern sky the Great Bear gradually rises above the eastern areas.
The following graphic shows the view of the sky on December 15 at 10 pm.