Mars in opposition to the Sun
On December 8, 2022, Mars will reach its opposition to the Sun in the constellation Taurus. It will then be exactly opposite the Sun in the sky and come particularly close to the Earth. Around 81.5 million kilometers separate us from it. With a brightness of -1.9 mag, it does not come close to Jupiter, but it is still brighter than any star. At the end of the year, it had already moved 94.6 million kilometers away from us, its brightness had decreased to -1.3 mag, which still makes it appear as bright as Sirius, the brightest fixed star in the evening sky, and the angular diameter of the Martian disk has decreased from 17 to 14.8 arc seconds.
The sun in December
On December 21, the sun reaches the southernmost and, for us, lowest point of its orbit. It is the beginning of winter.
During the month of December, the midday altitude of the sun varies by just 2 degrees. The sun is naturally at its lowest on December 21 at 17°21′. It then slowly rises again and reaches 17°42′ at the end of the year. December 21 is also the shortest day. The sun is above the horizon for eight hours.
Moon phases
The time around the full moon is unfavorable for astronomical observations. The December full moon is also very high and outshines the entire sky with its light. Only the brightest stars and the planets are still visible. As it rises later and later each day after the full moon, the observation conditions in the early evening hours will improve from day to day.
Stars and planets
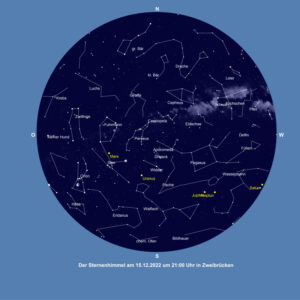 The map shows the starry sky on December 15 at 9 pm. This corresponds to the sky on December 1 at 10 pm and December 31 at 8 pm.
The map shows the starry sky on December 15 at 9 pm. This corresponds to the sky on December 1 at 10 pm and December 31 at 8 pm.
What is still visible of the summer constellations is low above the western horizon. These are mainly the Swan and Lyra. Pegasus, the most important part of the autumn square, has also moved far to the west. The Whale has now also made it to the western half of the sky. We find it in the southwest.
The eastern sky has been taken over by the winter constellations. Taurus and Taurus can no longer be overlooked. The Pleiades, the Pleiades, an open star cluster, also belong to Taurus. Gemini has already gained considerable height in the eastern sky. The sky hunter Orion is still low in the south-east. It is probably the most magnificent constellation of winter and should be familiar to everyone. The Orion Nebula below its belt stars, a gaseous nebula, can already be seen even in binoculars.
The sky also has a lot to offer in terms of planets. Saturn is already very low in the sky, but as dusk progresses it can still be seen clearly from 6 pm. Neptune, a telescopic object, can still be found in the telescope in the early evening hours and Jupiter, which outshines everything else, can be seen until late in the evening. In the last third of the month, the conditions for it will deteriorate significantly from 11 pm. Uranus is about to make its meridian passage and offers the best viewing conditions. We can see a small disk in the telescope. It is difficult to make out with the naked eye. Our neighboring planet Mars is high in the sky. Although it is not quite as bright as Jupiter, it outshines all other stars in terms of brightness. On December 8, it reaches this year's opposition to the sun and is therefore quite close to the Earth.
We can also see many meteors in the sky in December. Most of them are likely to belong to the Geminids, which have their maximum on December 14. They originate in the constellation Gemini. The Geminids are the strongest meteor stream of the year. Over 100 shooting stars can be seen in one hour. This puts them well ahead of the Perseids in August. But who wants to go to a shooting star party in December?
The star chart was created with the program Stargazer's Almanac for Windows by André Wulff.
